Product costs and period costs definition, explanation and examples
As you have arrived at the cost per unit of your products, you can use these numbers as a jumping-off point for determining their optimal selling prices. Now that we have taken a bird’s eye view of the matching principal, let’s look into the meanings of and difference between product costs and period costs. If you do not know how much your direct labor costs are in regards to these two sick employees, then you may not make the best decision in your hiring process. You cannot get your raw materials to the end of the production line without incurring costs.
Create a Free Account and Ask Any Financial Question
When combined with activity-based costing, product costing can be a powerful tool for running an even more efficient business. Managers may change product costs to remove the overhead component when making short-term production and sale-price decisions. A comprehensive understanding of product cost offers invaluable insights into how companies can optimize their operations for success. Also, properly managing costs can directly impact customer satisfaction, product quality, and profitability. Product cost management requires careful consideration of materials, labor, overhead expenses, research & development costs, marketing costs, and more.
Processing Decisions
These unsold units would continue to be treated as asset until they are sold in a following year and their cost transferred from inventory account to cost of goods sold account. Product cost, freshbooks vs quickbooks a crucial concept in cost accounting, refers to the total expenditure incurred to manufacture a product. This includes direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead costs.

Product Costing in 7 Easy Steps
- Indirect costs would include overhead such as rent and utility expenses.
- Manufacturing overhead includes all the costs related to the production process that are not direct materials or direct labor.
- With this information, you can make informed decisions about pricing strategies, potential profitability, and areas to optimize costs during the development process.
- A well-designed manufacturing process can avoid overproduction and excess storage costs.
Costs not included with factory overhead are selling costs and general administrative expenses. Fixed costs might include equipment, warehouse rent, labor, and utilities. You would add these costs together to determine the total cost and find average and marginal costs.
The balance of the manufacturing account discloses the total cost of goods manufactured, which is then transferred to the trading account. Jami Gong is a Chartered Professional Account and Financial System Consultant. She holds a Masters Degree in Professional Accounting from the University of New South Wales. Her areas of expertise include accounting system and enterprise resource planning implementations, as well as accounting business process improvement and workflow design.
In summary, the difference between product costs and period costs is that product costs are directly tied to the production of a specific product. In contrast, period costs are not directly connected to the production of a particular product and are expensed in the period in which they are incurred. However, it can be argued that depreciation is an indirect component of the cost of a product.
With careful research, accurate calculations, and proper consideration of all components, companies can calculate their product costs accurately. An average product cost per shirt of $103 is then determined by dividing the total annual product cost of $2.23 million by the annual production of shirts. The company should charge an amount higher than $103 per piece of its shirts.
Realizing profits is not simply determined by high prices or the sale of many units. For example, fixed costs for manufacturing an automobile would include equipment as well as workers’ salaries. That’s why product costing is a vital component of any thriving business.
Calculating product costs can be a difficult task, especially when it comes to determining the development costs of SaaS. However, there are some basic formulas to help calculate the product cost. Product cost plays a crucial role in determining the pricing strategy and overall profitability of a product or service. Product cost refers to the total expenses incurred during the development, production, and maintenance of a software product or technology solution. It encompasses a wide range of costs, including research, design, development, testing, deployment, and ongoing support and maintenance.
Consider lowering your raw material prices by adjusting the design of your product(s) and looking for less expensive alternatives. There are also fixed costs, such as rent, utilities, storage, and so on. The selling price is now higher compared to costs per unit, resulting in profits.
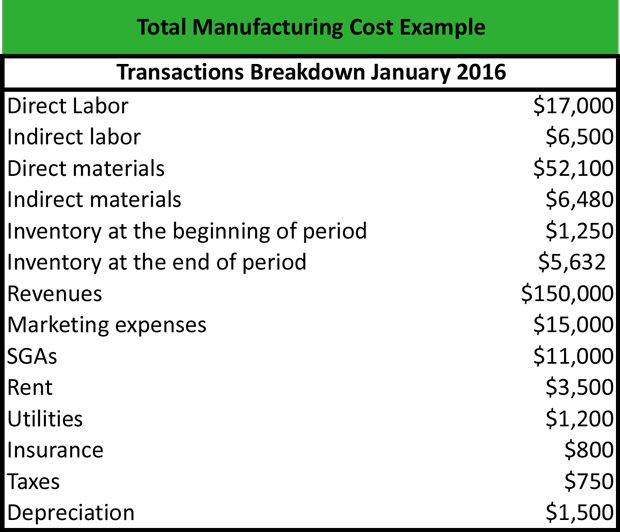
All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. As a partner, if you refresh your customers this calendar year, you can also still benefit from the XGS Deal Reg Booster for eligible deals to earn an extra 10% margin. They enjoy lower power bills since they recycle some waste material from the cane to generate electricity. To help you see how this can be implemented in an everyday manufacturing environment, consider the below examples. If you produce skimmed milk, cheese and whey protein, you can say that you have three projects running in your factory. Or even diversify by making cheese as your primary product and whey and casein as your secondary products.